You might be asking yourself why is my wifi so slow? It’s frustrating when your internet connection slows down, especially when you’re trying to stream a movie or finish an important task. According to High Speed Internet, nearly 45% of Americans report that their internet connection is too slow, but only 16% have upgraded their internet plans since the pandemic started. This shows that many people continue to struggle with sluggish internet without taking steps to improve it. But don’t worry, we are here to help! In this guide, we’ll explore the main reasons for slow internet and how to fix it, using simple terms. Let’s dive into what might be causing your slow Wi-Fi and how you can speed things up.

Why Is Your Internet So Slow?
Slow internet can happen for a number of reasons, and understanding the causes is the first step to fixing it. Here are some of the most common problems:
You Need to Restart Your Modem
Sometimes, restarting your modem is all it takes to fix slow internet. This is called "power cycling" and it can clear up temporary connection issues and refresh the modem’s memory. Here’s how to properly restart your modem:
Steps to Restart Your Modem:
- Turn off your modem: Look for the power button on the modem and press it to turn it off. If there’s no power button, simply unplug the modem from the power outlet.
- Wait for 10 to 30 seconds: This gives the modem time to fully shut down and reset. Waiting clears out its memory and any temporary glitches.
- Plug it back in or turn it back on: After waiting, press the power button again or plug the modem back into the power outlet.
- Wait for the modem to restart: The modem’s lights will blink as it reconnects. This can take anywhere from 1 to 5 minutes, depending on your modem and internet provider.
- Check your connection: Once the lights stabilize (usually solid green), test your internet connection by loading a webpage or using a speed test.
Restarting your modem every month can help maintain a faster, more reliable internet connection. If the problem persists, you may need to restart your router as well or contact your internet provider.
Your Provider’s Network Is Congested
Network congestion occurs when too many people are trying to use the internet at the same time, especially during peak hours, such as evenings when everyone is streaming, gaming, or working online. This overload can slow down the connection for everyone on the network, causing lag and buffering.
What Causes Network Congestion?
- Peak Hours: These typically occur between 7 PM and 11 PM when many people are at home streaming, gaming, or using other bandwidth-heavy activities. The high demand for data strains the network, leading to slower speeds.
- Shared Bandwidth: Internet service providers (ISPs) allocate bandwidth across multiple homes in the same neighborhood. When several users are online at once, they share the available bandwidth, which can slow down individual connections.
- ISP Throttling: Some ISPs intentionally slow down certain types of internet traffic during high-usage times to reduce strain on the network. This is often done with data-heavy activities like streaming or torrenting.
How to Identify Network Congestion
- Slower speeds during specific times: If your internet seems fine during the day but slows down drastically in the evening, it’s likely due to network congestion.
- Buffering while streaming: Services like Netflix, Hulu, or YouTube may pause to buffer during peak hours.
- Lag in online gaming or video calls: Multiplayer games and video conferencing apps may experience delays or interruptions due to slow internet during busy times.
How to Deal with Network Congestion
- Use the internet during off-peak hours: If possible, try scheduling downloads or online activities for early mornings or late at night when fewer people are online.
- Upgrade your internet plan: Higher-speed plans may offer more bandwidth, helping you avoid congestion issues, especially if multiple people in your household are using the internet at the same time.
- Use a VPN: Some people find that using a virtual private network (VPN) helps bypass ISP throttling, allowing for more consistent speeds.
- Switch ISPs: If network congestion is a consistent problem in your area, switching to a provider with fewer users or a higher data cap could improve your internet experience.
If congestion is a recurring issue, you may want to contact your ISP to inquire about local traffic or consider upgrading to fiber internet, which generally handles traffic better than cable or DSL networks.
Your Internet Plan’s Maximum Speed
If you’ve signed up for a basic internet plan, it might not be fast enough for all your devices, especially if you’re streaming or gaming. Find out if your internet speeds are up for your tasks!
Your Upload and Download Speeds
Your internet's performance is largely determined by two key factors: download speed and upload speed. These speeds directly affect how smoothly you can browse the web, stream videos, or upload files. If either of these speeds is slow, it can make your internet feel sluggish.
Download Speed
- What is it?
- Download speed refers to how quickly your internet connection can pull data from the web to your device. This includes activities like streaming videos, loading websites, and downloading files.
- Why it matters: A fast download speed is crucial for things like watching Netflix, YouTube, or playing online games. If your download speed is too low, you’ll experience buffering, slow-loading web pages, and delays in downloading files.
- Common download speed needs:
- Streaming HD videos: Requires about 5-8 Mbps.
- Streaming 4K videos: Can require 25 Mbps or more.
- Online gaming: Usually needs at least 3-6 Mbps, but low latency is also essential for smooth gameplay.
Upload Speed
- What is it?
- Upload speed measures how fast you can send data from your device to the internet. This includes sending emails, uploading videos to social media, or participating in video calls.
- Why it matters: If your upload speed is too slow, it will take longer to send files or experience lag during video conferencing (e.g., Zoom, Skype). Slow upload speeds are especially frustrating for activities like uploading large files to cloud storage or streaming content live.
- Common upload speed needs:
- Video conferencing: Requires 1-3 Mbps for smooth video calls.
- Uploading videos or large files: The faster the upload speed, the quicker the process. A minimum of 5-10 Mbps is recommended for large files.
- Live streaming: This typically requires 3-6 Mbps for basic quality, but higher upload speeds are necessary for better quality streams (e.g., 10+ Mbps for HD).
Why Your Speeds Might Be Slow
- Your Plan's Speed Limit: Sometimes, slow speeds are simply because you're on a lower-tier internet plan. If your plan only offers speeds up to 25 Mbps, that’s the fastest you’ll get. Upgrading to a higher plan might be necessary for smoother performance.
- ISP Throttling: Internet Service Providers (ISPs) sometimes intentionally slow down speeds (called throttling) during peak times or for specific activities like streaming or torrenting.
- Congestion in Your Network: If many devices in your home are online at once, they can consume bandwidth, making both download and upload speeds slower.
- Old Equipment: Using outdated routers or modems that can’t handle modern speeds will bottleneck your connection, limiting how fast data can flow in and out of your network.
How to Improve Upload and Download Speeds
- Upgrade Your Internet Plan: If you’re constantly dealing with slow speeds, upgrading to a faster plan that offers more bandwidth can help.
- Use a Wired Connection: Ethernet (wired) connections are generally faster and more reliable than Wi-Fi, especially for activities requiring high upload speeds. Get ethernet cable installation near me.
- Limit Background Applications: Some apps or updates run in the background, consuming bandwidth without you realizing it. Close unused apps to free up bandwidth.
- Restart Your Modem and Router: A simple reboot can help reset your connection and improve speeds.
Understanding your upload and download speeds helps you gauge what kind of internet plan you need for your online activities. If you are looking into wiring your connection our experts are specially trained in ethernet cable installation services and can help get your project done properly! If your speeds don’t match your needs, adjusting your equipment, plan, or setup can make a big difference.
Your Internet Connection Type
Your internet type matters. Fiber optic connections are faster than cable, DSL, or satellite. If you’re on a slower connection type, your speeds might be limited.
Why Is Your Wi-Fi So Slow?
Now that we’ve talked about the internet in general, let’s focus on Wi-Fi specifically. Wi-Fi can slow down for several reasons:
You Need to Restart Your Router
Your router is the gateway between your devices and the internet. Just like your modem, it can sometimes run into issues that cause your connection to slow down or drop. Restarting your router can help clear up minor technical problems and improve your internet speed.
Why Restarting Your Router Helps
- Clears Temporary Glitches: Over time, your router can accumulate temporary bugs or errors from handling network traffic. A restart clears these glitches and refreshes its system.
- Resolves IP Conflicts: If several devices on your network are assigned the same IP address, it can cause conflicts that slow down your internet. Restarting your router reassigns IP addresses and eliminates these issues.
- Improves Speed and Stability: Continuous usage can cause your router’s memory to fill up, reducing its ability to manage data efficiently. A reboot frees up that memory, making your connection faster and more stable.
- Refreshes Your Connection with the ISP: Restarting your router reconnects it to your ISP’s servers, which can solve connection issues that may have developed between your router and the provider.
Steps to Properly Restart Your Router
- Turn Off Your Router: Find the power button on your router and turn it off. If it doesn’t have a power button, unplug it from the power source.
- Wait for 30 Seconds: It’s important to wait for at least 30 seconds to allow the router’s memory to completely clear. This ensures a fresh restart.
- Turn the Router Back On: Press the power button again or plug it back into the outlet. The lights on your router will start blinking as it reconnects to the internet.
- Wait for the Router to Fully Reconnect: It may take a minute or two for the router to fully reboot. Once all the lights are back on and stable, try using the internet again to see if the speed has improved.
When Should You Restart Your Router?
- Regular Maintenance: To keep your network running smoothly, restart your router once a month. This helps clear out any minor issues before they become big problems.
- After a Power Outage: If your power goes out, your router may not reconnect to the internet automatically. A restart will help re-establish the connection.
- When You Notice Slow Speeds: If your Wi-Fi is noticeably slower than usual or you experience frequent dropouts, a quick restart could fix the problem.
Additional Tips for Router Health
- Check for Firmware Updates: Like other tech devices, routers need occasional updates to improve performance and security. Log into your router’s admin settings to check if it needs an update.
- Place Your Router in an Open Area: If your router is tucked away in a corner or behind walls, its signal strength can weaken. Make sure it’s placed in a central, elevated location for the best Wi-Fi coverage.
Restarting your router is a simple but effective way to resolve many Wi-Fi issues. If restarting doesn’t solve the problem, you might need to look into upgrading your router or contacting your internet provider.
Your Home Network Is Congested
In today's connected world, most homes have numerous devices linked to the internet, from smartphones and laptops to smart TVs and security cameras. When too many devices are connected to your Wi-Fi at the same time, the network becomes congested, which can slow down your overall internet speed. Which might be the reason why you are asking yourself why your wifi is so slow! This happens because each device consumes part of your available bandwidth, and when that bandwidth is stretched too thin, all devices experience slower speeds.
Why Does Congestion Happen?
- Limited Bandwidth: Your internet plan comes with a set amount of bandwidth (measured in Mbps). Each device connected to the internet—whether it’s streaming, downloading, or even just idling—uses a portion of that bandwidth.
- Heavy Data Usage: Some devices, like those used for streaming HD videos, playing online games, or video conferencing, require a significant amount of bandwidth. If multiple people are engaging in these activities simultaneously, they can hog the available data and leave less for other tasks, slowing down the entire network.
- Background Activity: Devices often run background applications that quietly use your internet, such as automatic updates or cloud backups. This hidden usage contributes to congestion without you even realizing it.
Signs of Home Network Congestion
- Slow Speeds Across Devices: If every device in your home is experiencing sluggish internet performance—whether it’s buffering during streaming or lagging in online gaming—network congestion is likely the culprit.
- Inconsistent Performance: You may notice that your internet speeds vary throughout the day, often slowing down during peak usage times when more devices are online.
- Buffering and Lag: Streaming services, online gaming, and video conferencing may buffer or lag when too many devices are competing for bandwidth.
How to Reduce Home Network Congestion
- Limit the Number of Devices Connected: Disconnect devices that aren’t being used. For instance, if your smart TV, tablet, and multiple phones are all connected but not in use, turning off their Wi-Fi can free up bandwidth.
- Use Quality of Service (QoS) Settings: Many modern routers come with QoS settings, which allow you to prioritize certain devices or types of activities, like streaming or gaming, over others. This ensures that your most important tasks get the bandwidth they need, even if many devices are connected.
- Create a Guest Network for Visitors: If friends or family are visiting and using your Wi-Fi, set up a guest network. This isolates their devices from your main network and limits how much bandwidth they consume, preventing congestion on your primary devices.
- Schedule Data-Intensive Tasks for Off-Peak Hours: If you need to download large files or run cloud backups, schedule these tasks for times when fewer people are online, like late at night or early in the morning.
- Upgrade Your Router: If you have a lot of devices, an older router may struggle to keep up with demand. Newer routers are designed to handle multiple devices more efficiently, offering features like dual-band or tri-band functionality to distribute bandwidth better.
- Upgrade Your Internet Plan: If network congestion is a frequent issue in your home, upgrading to a higher-speed internet plan with more bandwidth can help ensure that all devices get a fair share of speed without slowing down the network.
When Is Network Congestion Likely to Occur?
- Evenings and Weekends: Peak hours, especially in the evening when people are home from work or school, are the most common times for network congestion.
- During Large File Uploads/Downloads: If one or more devices are downloading large files, updating software, or backing up data to the cloud, this can take up significant bandwidth, slowing down the internet for everyone else.
By managing your devices and bandwidth usage effectively, you can reduce network congestion and enjoy a smoother, faster internet connection throughout your home. If issues persist, it might be time to consider upgrading your internet equipment or plan.
Use QoS Settings to Prioritize Certain Online Activities
Quality of Service (QoS) is a feature available on many modern routers that allows you to control how your internet bandwidth is distributed across devices and activities. By using QoS settings, you can ensure that important tasks, such as streaming videos, gaming, or video conferencing, get the priority they need to function smoothly, even when multiple devices are competing for bandwidth.
What Is QoS and Why Does It Matter?
QoS is a system that allows you to prioritize certain types of traffic on your network. For example, if you often experience lag while gaming or buffering during streaming because someone else is downloading large files, you can use QoS to give more bandwidth to your gaming or streaming activities.
Here’s why it matters:
- Prevent Bandwidth Hogging: If certain devices or applications are using too much bandwidth, they can slow down the internet for everyone else. QoS helps balance this by limiting the bandwidth available to lower-priority tasks, ensuring high-priority activities run smoothly.
- Improve Latency for Time-Sensitive Tasks: QoS can improve the performance of time-sensitive tasks like online gaming or video calls by ensuring they have low latency (the delay in data transfer). This makes your connection more responsive.
How Does QoS Work?
QoS settings allow you to categorize internet traffic into different types, such as:
- Streaming video (Netflix, YouTube, etc.)
- Online gaming (Xbox, PlayStation, PC games)
- Web browsing
- File downloads and cloud backups
You can assign priority levels to these categories—high, medium, or low—and your router will ensure that high-priority activities get more bandwidth. For example, if you set video conferencing as a high priority and file downloads as low, the router will allocate more speed to video calls, ensuring smooth, uninterrupted sessions.
Steps to Set Up QoS on Your Router
- Log Into Your Router's Admin Page: Open a web browser and type your router’s IP address into the address bar (commonly 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1). You’ll be prompted to enter your login credentials (usually found on the router or in its manual).
- Find QoS Settings: In the admin panel, look for a section labeled "QoS" or "Traffic Management." This is where you’ll find options for prioritizing activities.
- Choose the Devices or Applications to Prioritize: Depending on your router, you may be able to prioritize specific devices (e.g., your gaming console) or certain types of traffic (e.g., video streaming or gaming). For example, you can assign higher priority to your smart TV when watching Netflix or to your gaming PC when playing online games.
- Set Priority Levels: Most QoS systems allow you to assign priority levels (high, medium, or low) to various devices or activities. Simply drag and drop or select the ones you want to prioritize.
- Apply and Save: After setting your priorities, make sure to save your changes. Your router will now manage bandwidth according to the rules you’ve set.
Benefits of Using QoS
- Smoother Streaming: If you regularly stream content, QoS can prevent buffering, ensuring that you get uninterrupted video playback even when other devices are using the internet.
- Lag-Free Gaming: For gamers, QoS can dramatically reduce lag by prioritizing gaming traffic, improving your response time in multiplayer games.
- Seamless Video Calls: QoS can help keep video calls clear and lag-free by prioritizing video conferencing apps like Zoom or Skype over other less important tasks.
- Efficient Use of Bandwidth: By balancing your network traffic, QoS ensures that your available bandwidth is used efficiently, without one activity hogging all the speed.
When Should You Use QoS?
- In a Multi-Device Household: If many people in your home are using the internet at the same time for different activities (e.g., gaming, streaming, working), QoS can help ensure that everyone gets the necessary bandwidth for their tasks.
- When You Experience Lag or Buffering: If you frequently notice lag during gaming or buffering while streaming, QoS can prioritize these activities, giving them more bandwidth and reducing interruptions.
- For Work-From-Home Setups: If you work from home and rely on video calls or file uploads, you can prioritize these tasks to ensure a stable connection during important meetings.
Common QoS Settings to Look For
- Application-Based QoS: Some routers allow you to prioritize traffic based on specific applications (e.g., Skype, YouTube, or Fortnite).
- Device-Based QoS: This setting allows you to assign priority to specific devices on your network, such as a laptop, gaming console, or smart TV.
- Dynamic QoS: Some advanced routers offer dynamic QoS, which automatically adjusts bandwidth distribution based on the current needs of the devices connected to the network.
By using QoS settings, you can take control of your home network and ensure that critical activities get the bandwidth they need, providing a smoother and faster internet experience for everyone in your household.
Prune Your Internet Connections
Disconnect devices you’re not using. Fewer devices mean more speed for the ones that matter.
Put Visitors on a Guest Network
If you have guests using your Wi-Fi, set them up on a guest network so their usage doesn’t slow down your main connection. These settings can also be found on your routers admin page.
Check Your Router Location
Your router’s location plays a critical role in the strength and speed of your Wi-Fi signal. The router emits wireless signals in all directions, and obstacles like walls, furniture, and even appliances can block or weaken these signals. Placing your router in an optimal spot within your home can significantly improve your internet performance.

Why Router Location Matters
- Wi-Fi Signal Spread: Wi-Fi signals are broadcasted in a sphere around the router. If the router is placed in a corner or near thick walls, the signals can get blocked, causing poor connectivity in certain areas of your home.
- Interference from Objects: Metal objects, thick walls (especially those made of brick or concrete), and electronics like microwaves or cordless phones can interfere with Wi-Fi signals, reducing their strength and causing slower speeds.
- Distance from Devices: The farther your devices (e.g., laptops, smartphones) are from the router, the weaker the signal they receive. Signals degrade over distance, so if your router is far from where you use your devices most, you’ll experience slower speeds and more interruptions.
How to Optimize Router Placement
- Place It in a Central Location: The best spot for your router is as close to the center of your home as possible. This allows the signal to spread evenly throughout your living space, covering more areas effectively.
- Keep It Elevated: Placing your router on a shelf or mounting it on the wall can improve coverage. Wi-Fi signals tend to spread better downward, so having the router higher up ensures more areas receive stronger signals.
- Avoid Obstructions: Try to position your router away from thick walls, large furniture, or metal objects like filing cabinets. These materials can block or absorb Wi-Fi signals, leading to weaker connections in certain rooms.
- Stay Clear of Electronics: Devices like microwaves, baby monitors, and Bluetooth gadgets can interfere with your Wi-Fi signals because they operate on similar frequencies (2.4GHz). Make sure your router is placed far from these devices.
- Consider the Number of Floors: If your home has multiple stories, it’s a good idea to place the router on the floor where you use the internet most. Alternatively, you might consider using a Wi-Fi extender or mesh system to cover all floors evenly.
What Happens If the Router Is Poorly Placed?
- Dead Zones: A poorly located router can result in areas of your home where there is no Wi-Fi signal, also known as “dead zones.” These are common in homes where the router is placed far from high-use areas or blocked by large obstructions.
- Slower Speeds in Certain Rooms: If your router is stuck in a far-off corner or behind furniture, you may notice that certain rooms in your house receive slower speeds or struggle with loading pages, streaming, or gaming.
- Inconsistent Connectivity: You might experience frequent disconnects or weak signals in parts of your home if your router’s signal is blocked or degraded by its surroundings.
Additional Slow WiFi Tips for Improving Router Location
- Use a Mesh Wi-Fi System: If you have a large home with multiple rooms and floors, a mesh Wi-Fi system can help extend coverage by adding multiple nodes or satellite units throughout the house. This ensures a consistent connection no matter where you are.
- Experiment with Placement: If you’re experiencing slow speeds or dead zones, try moving your router to a new location and see if performance improves. Even small adjustments can make a big difference in coverage.
- Consider a Wi-Fi Extender: For larger homes or places where certain rooms struggle with coverage, a Wi-Fi extender can help amplify the signal. These devices boost your existing Wi-Fi network, pushing the signal into hard-to-reach areas.
By following these tips and optimizing your router's placement, you can ensure a stronger and more reliable Wi-Fi connection throughout your home. If your connection still struggles after repositioning, upgrading your router or considering a mesh network might be necessary. Our experts can help install and setup your wifi router.

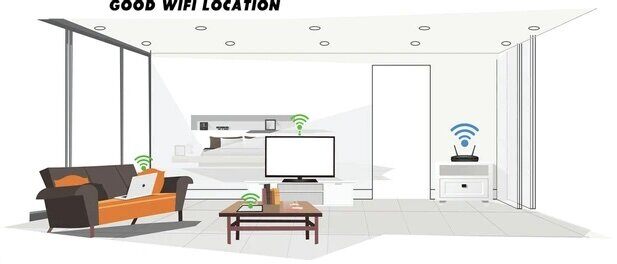
You Need a Stronger Wi-Fi Signal
If your signal is weak, your internet will be slow. Which is why you might be asking yourself why is my wifi so slow? Upgrading your router or using Wi-Fi extenders can help.
Wi-Fi Signal Interference
Other electronic devices, like microwaves and Bluetooth, can interfere with your Wi-Fi signal which will cause slow wifi. Keep your router away from them to improve speed.
Your Networking Cables Are Loose or Damaged
Loose or damaged cables connecting your modem or router can lead to a slow internet. Check them and replace if necessary.
You Have High Latency
Latency, often referred to as “ping,” is the time it takes for data to travel from your device to a server and back again. Unlike download and upload speeds, which measure how fast data moves, latency measures how long it takes for that data to start moving. High latency can cause slow internet, even if your internet speeds (download and upload) are otherwise good.
What Causes High Latency?
- Distance to the Server: The farther the server you're connecting to is located, the longer it takes for data to travel back and forth. For instance, if you're playing an online game on a server halfway across the world, you'll likely experience higher latency than if the server were closer to your location.
- Network Congestion: When many people are using the internet simultaneously—either within your home or in your neighborhood—your internet connection may slow down, increasing latency. This is because the network has to handle more data, causing delays in the response time.
- Wi-Fi Interference: Wireless connections are more prone to interference, which can cause delays. Things like walls, electronics, and even other Wi-Fi networks can interfere with your connection and increase latency and slow wifi speeds.
- Old or Overloaded Equipment: Using outdated routers or modems, or connecting too many devices to the same network, can cause delays in data transmission, resulting in higher latency.
- Server Overload: If the server you are trying to connect to is handling too many users, it may take longer to respond to your requests, causing high latency.
Signs of High Latency
- Lag in Online Gaming: If you’re playing an online game and experiencing delays between your actions and the server's response (for example, delayed movements or shots), high latency is usually the issue.
- Delayed Video Calls: During video conferencing, high latency can cause noticeable delays between when someone speaks and when the audio or video reaches the other participants.
- Slow Web Browsing: Pages may take longer to load, not because of slow download speeds, but because your request to access the webpage is delayed.
- Buffering During Streaming: Although more commonly attributed to slow download speeds, high latency can also contribute to buffering, especially when streaming live events.
How to Reduce High Latency
- Switch to a Wired Connection: Ethernet cables offer a more stable and faster connection compared to Wi-Fi, as they are less prone to interference. This can help reduce latency significantly, especially for gaming or video conferencing.
- Reduce Network Congestion: Limiting the number of devices connected to your network or scheduling high-bandwidth activities (such as large downloads or video streaming) for off-peak hours can help reduce latency.
- Use a Local Server: For online gaming or file sharing, connect to servers that are geographically closer to you. The shorter the distance, the lower the latency.
- Upgrade Your Router: If your router is old or struggling to manage multiple devices, upgrading to a newer model with better technology (such as dual-band or tri-band routers) can help reduce latency.
- Check for Background Programs: Ensure no unnecessary apps are running in the background on your devices, consuming bandwidth and increasing latency.
- Contact Your ISP: Sometimes, high latency is due to network issues with your Internet Service Provider (ISP). If you're consistently experiencing high latency, contact your ISP to see if they can offer a solution or upgrade your plan.
When High Latency Is Unavoidable
High latency may be unavoidable in certain situations, such as:
- Satellite Internet: This type of internet has inherently high latency due to the long distance data must travel to and from satellites in space.
- Long-Distance Connections: If you need to connect to a server located across the globe (e.g., accessing a website hosted on another continent), you may experience higher latency no matter your local setup.
By understanding the causes and solutions for high latency, you can better manage your internet connection and enjoy smoother online experiences. If you're noticing delays in gaming, video calls, or general browsing, addressing latency could be the key to speeding things up.
Your Devices Need an Update or Are Outdated
Old or outdated devices may not work well with modern routers, slowing down your Wi-Fi. Update your devices to improve performance to fix the reason why your wifi is so slow.
Background Applications Consuming Bandwidth
Your internet connection may seem slower than expected because some apps or updates are running in the background, silently consuming a significant portion of your bandwidth. This can affect all your devices, including computers, phones, tablets, and even smart home gadgets. These background activities can range from automatic software updates to cloud backups and data syncing, all of which use your internet connection without you realizing it. Which could be the reason why your wifi is so slow.
How Background Apps Affect Slow WiFi
- Automatic Updates: Many devices automatically download software and security updates in the background. These updates can consume a lot of bandwidth, especially if multiple devices are updating at the same time. For example, operating system updates or app updates on your smartphone, laptop, or gaming console can use up valuable bandwidth.
- Cloud Backups: Services like Google Drive, Dropbox, iCloud, or OneDrive often run in the background, syncing and backing up files. While this is important for keeping your data safe, it can slow down your internet speed, especially if large files are being uploaded or synced.
- Streaming Apps Running in the Background: Apps like Netflix, YouTube, or Spotify might continue to stream or buffer content in the background, even when you’re not actively using them. This constant data consumption can significantly slow down other online activities.
- Online Gaming Downloads: Some games or gaming platforms (e.g., Steam, Xbox, or PlayStation) automatically download updates or patches, which can consume large amounts of bandwidth, making your Wi-Fi slower for other devices.
- Background Tabs and Browser Extensions: Even keeping multiple tabs open in your web browser can slow down your internet. Many websites constantly refresh or download data in the background, consuming bandwidth without you noticing. Additionally, certain browser extensions might constantly fetch data, slowing down your connection further.
How to Identify Background Bandwidth Hogs
- Check Task Manager (Windows) or Activity Monitor (Mac): On your computer, you can use Task Manager (press Ctrl + Shift + Esc) on Windows or Activity Monitor on Mac to see which applications are using the most bandwidth. These tools display real-time data on what’s running in the background and how much internet each app is using.
- Check Your Router’s Admin Panel: Many modern routers allow you to log in to a control panel where you can monitor bandwidth usage by device. This lets you identify if a specific device or app is consuming an unusually large amount of bandwidth.
- Monitor Data Usage on Mobile Devices: On smartphones, you can go to your device's settings (under “Data Usage” or “Network”) to see which apps are using the most data. This can help you identify background apps that might be draining bandwidth.
How to Reduce Bandwidth Usage from Background Apps
- Turn Off Automatic Updates: Most devices allow you to schedule updates or turn off automatic updates entirely. For example, on your computer or smartphone, you can set updates to only download when you manually approve them. This can prevent large downloads from hogging bandwidth during busy internet use periods.
- Pause Cloud Syncing: If you don’t need constant cloud backups, you can pause or schedule syncing for times when you’re not using the internet. For example, services like Google Drive, Dropbox, and OneDrive let you adjust settings so that backups occur only when needed.
- Close Unnecessary Tabs and Apps: Simply closing unused browser tabs and apps that are running in the background can free up bandwidth. Make sure to fully close apps instead of just minimizing them, as they might still consume data in the background.
- Disable Background App Refresh: On mobile devices, you can turn off “Background App Refresh” in the settings. This will stop apps from using data when they’re not actively being used. For iPhones, this is found under "Settings > General > Background App Refresh," while for Android, it's usually under "Settings > Data usage."
- Limit Streaming and Gaming Updates: Streaming apps often buffer content in the background. Make sure to pause or exit the app when you’re not actively watching or listening. Similarly, check gaming platforms for settings that allow you to control automatic downloads and updates.
Why Reducing Background Bandwidth Matters
- Improves Speed for Other Devices: By cutting down on bandwidth used by background apps, you free up internet speed for other tasks, such as streaming or video calls.
- Saves Data: For those on capped internet plans, reducing background usage can prevent you from reaching your data limit too quickly, helping you avoid extra charges.
- Reduces Network Congestion: When multiple devices in your home are constantly consuming bandwidth, network congestion can occur. Closing background apps helps ensure that more bandwidth is available for critical tasks.
By regularly checking and managing the apps and services running in the background, you can ensure that your internet connection is running at its optimal speed, improving overall performance across all your devices.
Malware or Viruses

Malware and viruses can have a significant impact on your internet speed and overall device performance. These malicious programs often run in the background, consuming valuable resources such as bandwidth, memory, and processing power. Not only can they be the reason why your wifi is so slow, but they can also use your internet connection for their own purposes, like sending out spam emails, performing data theft, or participating in distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks.
How Malware Affects Slow Internet Speed
- Background Activity: Once infected with malware, your device may perform tasks in the background that you’re unaware of. These tasks can include sending data to other servers or receiving instructions from hackers, all of which consume your internet bandwidth and slow down your connection.
- Spyware and Adware: Some types of malware, like spyware and adware, are designed to track your browsing habits or display unwanted ads. These programs frequently send and receive data to remote servers, which can result in sluggish internet performance as they consume bandwidth.
- Botnets: Malware can also turn your device into part of a botnet—a network of infected devices controlled by a hacker. These botnets use your internet connection to carry out large-scale cyber-attacks or send spam, significantly reducing your available bandwidth and making your internet slow.
- Increased CPU Usage: Malware may use your device's CPU power for cryptocurrency mining or running other intensive processes. This reduces the amount of resources available to run your legitimate programs, causing delays and slow performance that also affect your internet browsing experience.
How to Detect Malware or Viruses
- Sluggish Performance: If your device suddenly becomes much slower than usual—whether it’s taking a long time to open apps or web pages are loading slowly—it could be a sign of malware. This slowdown often includes both device processing speed and internet performance.
- Unexpected Ads or Pop-Ups: An increase in unwanted pop-up ads, even when you're not browsing the web, could indicate adware on your device. These ads not only consume bandwidth but can also expose you to more malware if clicked.
- Unfamiliar Programs Running: If you notice strange applications or processes running on your device that you don’t recognize, malware could be the culprit. You can check this by looking at your Task Manager (Windows) or Activity Monitor (Mac) to see which processes are using your internet bandwidth.
- Frequent Crashes or Freezes: Devices infected with malware may experience frequent crashes, errors, or freezes due to the extra strain malware puts on your system’s resources.
How to Protect Your Device from Malware
- Install Antivirus Software: One of the best defenses against malware is reliable antivirus software. Antivirus programs can detect and remove malware before it has a chance to do serious damage. Be sure to keep your antivirus up to date so it can identify the latest threats.
- Perform Regular Scans: Make it a habit to run regular scans on your devices. This will help catch any malware that might have slipped through. Most antivirus software allows you to schedule automatic scans, ensuring your system is regularly checked without you having to remember.
- Keep Software Updated: Ensure that your operating system, browser, and other software are always updated to the latest versions. Security patches in updates often fix vulnerabilities that malware can exploit.
- Be Cautious When Downloading Files: Avoid downloading files or clicking on links from untrusted or unfamiliar sources. Malware is often hidden in email attachments, pop-up ads, or suspicious websites.
- Use a Firewall: A firewall adds another layer of protection by blocking unauthorized access to your device and monitoring incoming and outgoing internet traffic. Most operating systems come with a built-in firewall, so make sure it’s enabled.
- Use Strong Passwords and Two-Factor Authentication: Strengthen your device’s defenses by using complex passwords and enabling two-factor authentication wherever possible. This can help prevent unauthorized access to your accounts and systems, which could otherwise be compromised by malware.
How to Remove Malware
If you suspect your device has been infected, take the following steps to remove the malware:
- Run a Full Antivirus Scan: Open your antivirus software and perform a complete scan of your system. If it detects any threats, follow the instructions to remove them.
- Use Malware Removal Tools: If your regular antivirus program isn’t enough, there are specialized malware removal tools (like Malwarebytes) that focus on detecting and eliminating malicious software.
- Reset Your Browser: If the malware is affecting your browsing experience (e.g., showing pop-ups, redirecting you to unwanted websites), reset your browser to its default settings. This will remove any malicious extensions or settings that might have been altered by malware.
- Reinstall Your Operating System: In extreme cases where the malware deeply infects your system, reinstalling your operating system might be necessary to completely remove the threat. Make sure to back up important data before doing this.
By staying vigilant and using antivirus software to scan for malware regularly, you can protect your devices from infection and prevent malicious programs from hogging your bandwidth and slowing down your internet connection.
Our Favorite AntiVirus Software

Inefficient Internet Browser Settings
Sometimes, the reason why your wifi is so slow aren't the fault of your connection itself but are caused by inefficient browser settings. Over time, your web browser can accumulate clutter, such as cached files, cookies, and unnecessary extensions, which can slow down its performance. Optimizing your browser settings can help speed things up, improve page load times, and reduce frustration when browsing the web.
Common Browser Issues That Can Slow Down Your Internet
1. Accumulated Cache and Cookies:
- Cache: Your browser stores copies of websites you visit (called the cache) so that it can load them faster the next time. However, over time, this cache can become large and outdated, leading to slower browsing speeds.
- Cookies: These small data files store information about your online activity and preferences. While useful for maintaining session information (like keeping you logged into a website), an excessive number of cookies can bog down your browser’s performance.
2. Too Many Extensions:
- Browser extensions add functionality, but having too many active extensions can eat up system resources and slow down your browsing experience. Some extensions may also run background processes that consume bandwidth without you realizing it.
3. Outdated Browser Software:
- An outdated web browser may not be optimized for the latest web standards or security protocols, which can result in slower browsing and increased vulnerability to malware.
4. Open Tabs and Processes:
- Keeping too many tabs open at once can overwhelm your browser, causing it to slow down. Each tab consumes memory and may refresh in the background, using up bandwidth.
5. Inefficient Search Settings:
- Some browsers have default search settings that can send data requests to slower search engines or sites. Tweaking your search settings to use faster, more reliable engines can help improve load times.
How to Fix Inefficient Browser Settings
1. Clear Your Cache and Cookies:
- Why it helps: Clearing your cache and cookies can free up space and remove outdated or corrupt files that slow down your browser.
- How to do it:
- In Chrome: Go to Settings > Privacy and security > Clear browsing data. Select "Cached images and files" and "Cookies and other site data," then click "Clear data."
- In Firefox: Go to Settings > Privacy & Security > Cookies and Site Data, and click "Clear Data."
- In Safari: Go to Preferences > Privacy > Manage Website Data, then select "Remove All."
2. Disable or Remove Unnecessary Extensions:
- Why it helps: Extensions, while helpful, can slow down your browser if too many are installed or if they run continuously in the background.
- How to do it:
- In Chrome: Go to Settings > Extensions and toggle off or remove unnecessary extensions.
- In Firefox: Go to Add-ons and Themes > Extensions, and disable or remove the ones you no longer use.
- In Safari: Go to Preferences > Extensions, and uncheck any that are no longer needed.
3. Update Your Browser:
- Why it helps: Keeping your browser up to date ensures that it’s using the latest speed optimizations, security patches, and bug fixes.
- How to do it:
- Most modern browsers update automatically, but you can manually check for updates by going to your browser’s settings or “About” section.
4. Limit the Number of Open Tabs:
- Why it helps: Closing unnecessary tabs frees up system resources and memory, allowing your browser to run more efficiently.
- How to do it: Close any tabs you're not actively using or use a browser feature like tab groups or tab hibernation to reduce the resource consumption of inactive tabs.
5. Change Search Engine Settings:
- Why it helps: Setting your browser to use a fast, efficient search engine (like Google or Bing) as the default can improve page load times.
- How to do it:
- In Chrome: Go to Settings > Search engine and select your preferred search engine.
- In Firefox: Go to Settings > Search, and select a search engine from the default list.
- In Safari: Go to Preferences > Search and select a search engine.
Additional Browser Optimization Tips
- Enable Browser Compression: Some browsers support data compression techniques (such as Google Chrome’s Data Saver) to reduce the amount of data loaded, speeding up your connection.
- Turn Off Autoplay Videos: Many websites automatically play videos in the background, which can consume bandwidth. Most browsers allow you to disable autoplay in their settings.
- Enable Hardware Acceleration: If your computer has a powerful GPU (graphics processing unit), enabling hardware acceleration can help improve browser performance, especially when streaming videos.
Why Improving Browser Efficiency Matters
- Faster Browsing: By removing the clutter in your browser, you allow it to load pages faster, improving your overall internet experience.
- Improved Device Performance: A browser that’s optimized uses fewer system resources, freeing up your computer’s memory and processing power for other tasks.
- Better Security: Regularly clearing cookies and updating your browser also helps protect your privacy and ensures you’re using the latest security measures against malware.
Optimizing your browser settings is a simple yet effective way to boost your internet speed without changing your connection. Regularly clearing your cache, updating your browser, and managing extensions can go a long way toward improving your online experience.
How to Fix Slow Internet
Now that you know what could be causing your slow internet, let’s look at how to fix it.
First, Know Your Plan Speed
Check what internet speed you’re paying for. If your plan doesn’t offer enough speed, you may need to upgrade.
Next, Run a Speed Test and Compare
Use a speed test tool, such as https://www.speedtest.net/, to check your current internet speed and compare it with your plan. If it’s lower, there may be a problem.
Check for Wi-Fi Dead Zones
Some areas in your home may not get a strong signal. Move your router or use extenders to cover those spots. If you need professional help identifying dead spots and how to expand your wifi routers signal we can help!
Reorganize Your Wi-Fi Connections
Limit how many devices are using Wi-Fi at once. Disconnect devices you aren’t using.
Change Your Wi-Fi Band’s Channel
Your Wi-Fi network operates on different frequency bands, usually 2.4GHz and 5GHz, and these bands are divided into channels. If too many nearby Wi-Fi networks are operating on the same channel, interference can occur, which can slow down your internet. This is common in densely populated areas, like apartment buildings, where many routers compete for the same wireless channels. Changing your Wi-Fi channel can help improve speed and reduce interference.
Why Wi-Fi Channels Matter
- Channel Congestion: Wi-Fi signals travel through radio frequencies, and when too many devices or networks use the same channel, it becomes congested. This is like driving on a crowded highway—more traffic leads to slower speeds for everyone. If your network is competing with your neighbors' networks on the same channel, you might experience slower speeds, dropped connections, or higher latency.
- 2.4GHz vs. 5GHz Bands: The 2.4GHz band has fewer available channels (typically 11 in North America) and is more prone to interference because many devices—like microwaves and Bluetooth gadgets—also use the same frequency. The 5GHz band, on the other hand, has many more channels and is less crowded, making it a better choice for faster speeds and less interference.
How to Check for Channel Congestion
- Use a Wi-Fi Analyzer: You can use apps like Wi-Fi Analyzer (for Android) or tools like NetSpot (for macOS/Windows) to scan your area and see which Wi-Fi channels are most congested. These apps will show you which channels are being used by nearby routers and help you identify less crowded channels.
- Check Your Router’s Admin Page: Some modern routers have built-in tools that automatically detect the least congested channel. You can find this in the router’s settings, usually under the wireless or advanced settings section.
Steps to Change Your Wi-Fi Channel
1. Access Your Router’s Admin Page:
- Open a web browser and type your router’s IP address into the address bar (commonly 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1). Enter your login credentials—usually found on the router or in its manual.
2. Find the Wireless Settings Section:
- Look for a section labeled Wireless Settings, Wi-Fi Settings, or Advanced Settings.
2.1 Select a Channel:
- For the 2.4GHz band, choose a channel that’s least congested. The best channels to use are usually 1, 6, or 11 because they don’t overlap with each other.
- For the 5GHz band, you have many more channels to choose from, and interference is less of an issue. Your router may automatically select the best channel, or you can manually choose one based on your Wi-Fi analyzer results.
2.2 Save and Apply the Changes:
- After selecting the channel, save your changes and restart your router if necessary. This will apply the new channel settings.
Benefits of Changing Your Wi-Fi Channel
- Reduced Interference: By switching to a less congested channel, you reduce interference from neighboring networks and devices, leading to a stronger and more stable connection.
- Improved Speeds: Less interference means your router can communicate with your devices more efficiently, which can improve your internet speeds, especially for tasks like streaming and gaming.
- Better Reliability: A less congested channel reduces the chances of dropped connections, ensuring a more reliable Wi-Fi experience across your home.
Additional Tips for Optimizing Your Wi-Fi
- Dual-Band Routers: If you have a dual-band router, you can assign certain devices to the 5GHz band and others to the 2.4GHz band. This spreads out the traffic and reduces congestion on each band.
- Automatic Channel Selection: Some modern routers automatically select the best channel for you. However, manually changing the channel can still be beneficial in some cases if the router isn’t picking the optimal one.
- Regularly Check for Congestion: Wi-Fi channel usage can change over time, especially if more neighbors set up new routers. It’s a good idea to periodically check your channels and switch if needed.
Changing your Wi-Fi channel is a simple yet effective way to improve your network’s performance, especially if you live in a crowded area. By following these steps, you can avoid interference and enjoy faster, more stable internet. You can also have once of our network troubleshooting experts help fix the issue for you!
Check Connected Devices
Too many connected devices can slow down your internet. Limit the number of devices on your network.
Quick Fixes for Slow Internet Speeds

If you’re still having trouble, here are some quick fixes:
Fix #1: Power Cycle Your Modem and Router (or Wireless Gateway)
Turn off your modem and router for 30 seconds, then turn them back on. This often solves connection issues.
Fix #2: Move Your Router to Another Location
Try placing your router in a more central location in your home for better coverage.
Fix #3: Use the Internet During Off-Peak Hours
If your provider’s network is congested, try using the internet at times when fewer people are online.
Fix #4: Upgrade Your Internet Plan
If your current plan isn’t fast enough for your needs, upgrading to a higher-speed plan may be the solution.
Fix #5: Try Another DNS Server
Sometimes, changing your DNS settings can help improve speed. You can switch to a public DNS like Google’s or Cloudflare’s for better performance.
How Do I Know if I Need a Faster Internet Plan?
If you frequently experience slow internet speeds, especially during high-demand activities like streaming or gaming, you might need a faster plan.
What Type of Internet Plan Is the Fastest?
Fiber-optic connections offer the fastest internet speeds, followed by cable. DSL and satellite are generally slower.






